Lucknow
Lucknow (, Lakhnaū) is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is also the second largest urban agglomeration in Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and division. Having a population of 2.8 million as per 2011 census, it is the eleventh most populous city and the twelfth-most populous urban agglomeration of India. Lucknow has always been a multicultural city that flourished as a North Indian cultural and artistic hub, and the seat of power of Nawabs in the 18th and 19th centuries. It continues to be an important centre of governance, administration, education, commerce, aerospace, finance, pharmaceuticals, technology, design, culture, tourism, music and poetry.
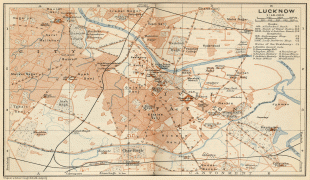
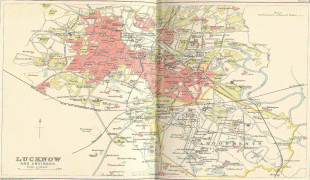
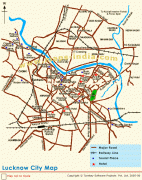
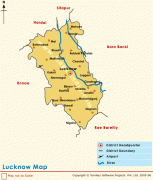
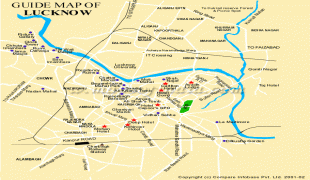
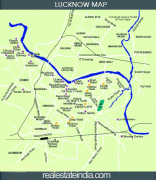
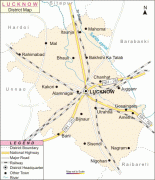
Lucknow stands at an elevation of approximately 123 m above sea level. The city had an area of 402 km2 until December 2019, when 88 villages were added to the municipal limits and the area increased to 631 km2. Bounded on the east by Barabanki, on the west by Unnao, on the south by Raebareli and in the north by Sitapur and Hardoi, Lucknow sits on the northwestern shore of the Gomti River. , there were 110 wards in the city. Morphologically, three clear demarcations exist: The Central business district, which is a fully built up area, comprises Hazratganj, Aminabad and Chowk. A middle zone surrounds the inner zone with cement houses while the outer zone consists of slums.
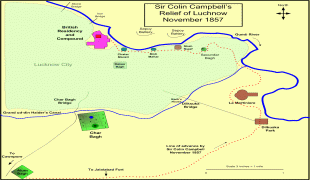
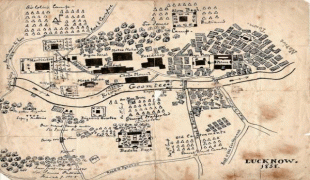
Historically, Lucknow was the capital of the Awadh region, controlled by the Delhi Sultanate and later the Mughal Empire. It was transferred to the Nawabs of Awadh. In 1856, the British East India Company abolished local rule and took complete control of the city along with the rest of Awadh and, in 1857, transferred it to the British Raj. Along with the rest of India, Lucknow became independent from Britain on 15 August 1947. It has been listed as the 17th-fastest growing city in India and 74th in the world.
Lucknow, along with Agra and Varanasi, is in the Uttar Pradesh Heritage Arc, a chain of survey triangulations created by the Government of Uttar Pradesh to boost tourism in the state.
"Lucknow" is the anglicised spelling of the local pronunciation "Lakhnau". According to one legend, the city is named after Lakshmana, a hero of the Hindu epic Ramayana. The legend states that Lakshmana had a palace or an estate in the area, which was called Lakshmanapuri (Sanskrit: लक्ष्मणपुरी, lit. Lakshmana's city). The settlement came to be known as Lakhanpur (or Lachhmanpur) by the 11th century, and later, Lucknow.
A similar theory states that the city was known as Lakshmanavati (लक्ष्मणवती,fortunate) after Lakshmana. The name changed to Lakhanavati, then Lakhnauti and finally Lakhnau. Yet another theory states that the city's name is connected with Lakshmi, the Hindu goddess of wealth. Over time, the name changed to Laksmanauti, Laksmnaut, Lakhsnaut, Lakhsnau and, finally, Lakhnau.
Lucknow stands at an elevation of approximately 123 m above sea level. The city had an area of 402 km2 until December 2019, when 88 villages were added to the municipal limits and the area increased to 631 km2. Bounded on the east by Barabanki, on the west by Unnao, on the south by Raebareli and in the north by Sitapur and Hardoi, Lucknow sits on the northwestern shore of the Gomti River. , there were 110 wards in the city. Morphologically, three clear demarcations exist: The Central business district, which is a fully built up area, comprises Hazratganj, Aminabad and Chowk. A middle zone surrounds the inner zone with cement houses while the outer zone consists of slums.
Historically, Lucknow was the capital of the Awadh region, controlled by the Delhi Sultanate and later the Mughal Empire. It was transferred to the Nawabs of Awadh. In 1856, the British East India Company abolished local rule and took complete control of the city along with the rest of Awadh and, in 1857, transferred it to the British Raj. Along with the rest of India, Lucknow became independent from Britain on 15 August 1947. It has been listed as the 17th-fastest growing city in India and 74th in the world.
Lucknow, along with Agra and Varanasi, is in the Uttar Pradesh Heritage Arc, a chain of survey triangulations created by the Government of Uttar Pradesh to boost tourism in the state.
"Lucknow" is the anglicised spelling of the local pronunciation "Lakhnau". According to one legend, the city is named after Lakshmana, a hero of the Hindu epic Ramayana. The legend states that Lakshmana had a palace or an estate in the area, which was called Lakshmanapuri (Sanskrit: लक्ष्मणपुरी, lit. Lakshmana's city). The settlement came to be known as Lakhanpur (or Lachhmanpur) by the 11th century, and later, Lucknow.
A similar theory states that the city was known as Lakshmanavati (लक्ष्मणवती,fortunate) after Lakshmana. The name changed to Lakhanavati, then Lakhnauti and finally Lakhnau. Yet another theory states that the city's name is connected with Lakshmi, the Hindu goddess of wealth. Over time, the name changed to Laksmanauti, Laksmnaut, Lakhsnaut, Lakhsnau and, finally, Lakhnau.
Map - Lucknow
Map
Country - India
 |
 |
| Flag of India | |
Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago. Their long occupation, initially in varying forms of isolation as hunter-gatherers, has made the region highly diverse, second only to Africa in human genetic diversity. Settled life emerged on the subcontinent in the western margins of the Indus river basin 9,000 years ago, evolving gradually into the Indus Valley Civilisation of the third millennium BCE. By, an archaic form of Sanskrit, an Indo-European language, had diffused into India from the northwest. (a) (b) (c), "In Punjab, a dry region with grasslands watered by five rivers (hence ‘panch’ and ‘ab’) draining the western Himalayas, one prehistoric culture left no material remains, but some of its ritual texts were preserved orally over the millennia. The culture is called Aryan, and evidence in its texts indicates that it spread slowly south-east, following the course of the Yamuna and Ganga Rivers. Its elite called itself Arya (pure) and distinguished themselves sharply from others. Aryans led kin groups organized as nomadic horse-herding tribes. Their ritual texts are called Vedas, composed in Sanskrit. Vedic Sanskrit is recorded only in hymns that were part of Vedic rituals to Aryan gods. To be Aryan apparently meant to belong to the elite among pastoral tribes. Texts that record Aryan culture are not precisely datable, but they seem to begin around 1200 BCE with four collections of Vedic hymns (Rg, Sama, Yajur, and Artharva)."
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| INR | Indian rupee | ₹ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| AS | Assamese language |
| BN | Bengali language |
| BH | Bihari languages |
| EN | English language |
| GU | Gujarati language |
| HI | Hindi |
| KN | Kannada language |
| ML | Malayalam language |
| MR | Marathi language |
| OR | Oriya language |
| PA | Panjabi language |
| TA | Tamil language |
| TE | Telugu language |
| UR | Urdu |